Client: City of Edmonton
Project Duration: 2014 – Ongoing
Pinchin Team: Mechanical Engineering Group
What is a District Energy Sharing System?
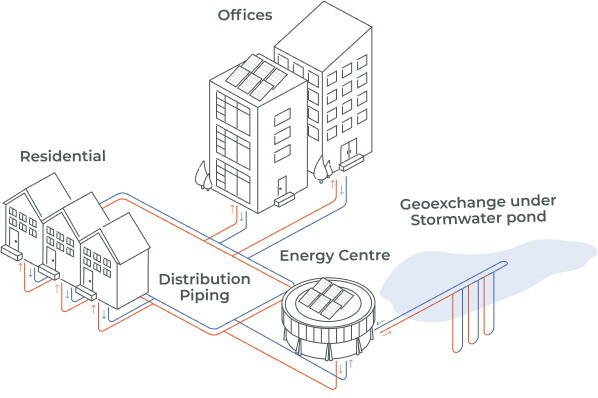
District Energy is a way to provide heating or cooling to multiple buildings in a community from a central energy source.
A District Energy Sharing System (DESS) is a type of District Energy that is optimized for renewable energy sources such as heat pumps, waste heat recovery, geoexchange, or wastewater heat recovery.
The system consists of an energy centre where thermal energy is extracted from a renewable source and then sent through a network of underground pipes to homes and buildings. In a DESS, every connected building has a heat pump for heating or cooling the space. The heat pumps extract heat from the DESS for heating, or return waste heat from cooling to the DESS. Unlike a traditional district heating or district cooling system, a DESS provides both heating and cooling.
It is called a Sharing system because energy is shared between buildings – waste heat from buildings in cooling is recovered and used to heat adjacent buildings. Sharing can reduce a community’s energy requirement by 20% or more.
District Energy is a proven technology that is used all over the world. In Canada, a number of other cities use district energy systems, and if we look even further to Europe, cities like Copenhagen have historically built systems where over 90% of the buildings are connected to a district energy system.
Project Background
Following the closure of the Edmonton City Centre Airport, the City of Edmonton approved a redevelopment plan for this 217-hectare parcel of land. Recognizing the increased economic, social, and environmental costs associated with conventional development approaches, the City selected Pinchin and our partners to create a world-leading district energy concept for the site. The City decided to develop an Ambient Temperature District Energy Sharing System. An ambient system was determined to offer higher efficiency, lower first costs, ability to provide cooling with heating, and better integration of renewable energy.
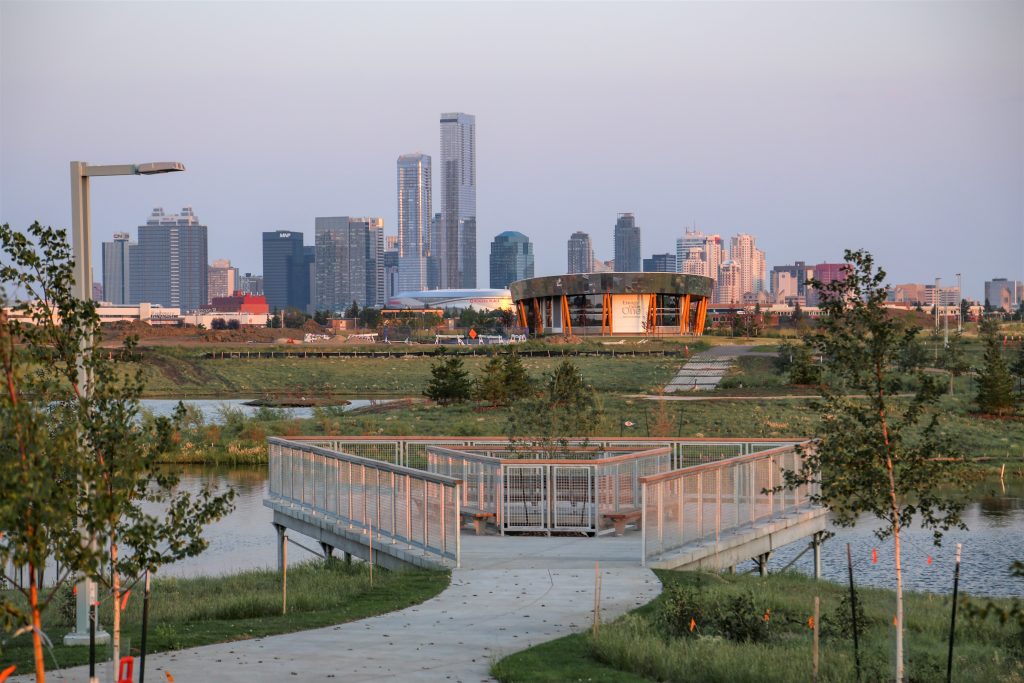

Source: Our Story – Blatchford (blatchfordedmonton.ca)
How the District Energy Sharing System works?
Source: Blatchford Renewable Energy: District Energy Sharing System – YouTube
How Pinchin Helped?
About the DESS Design
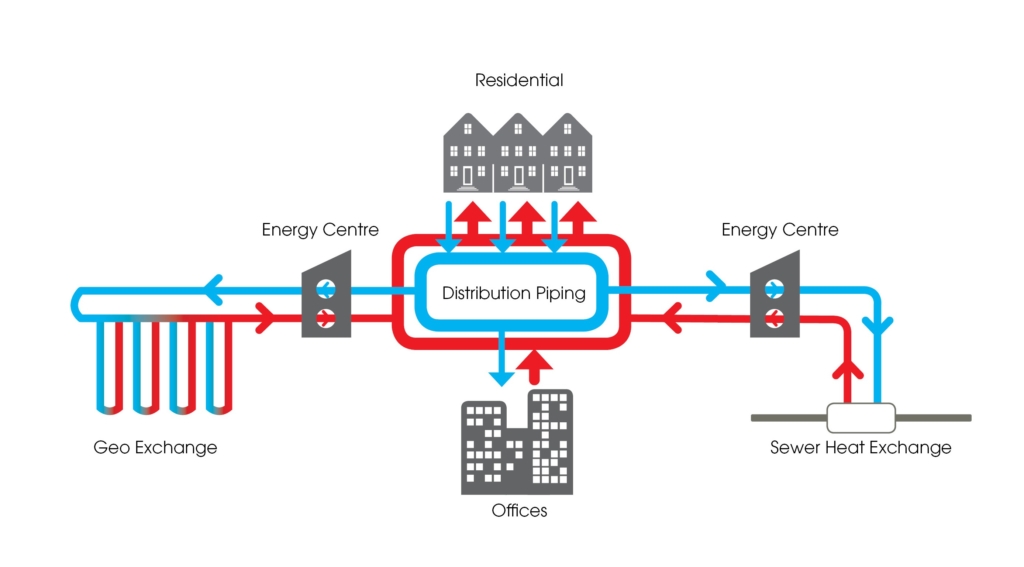
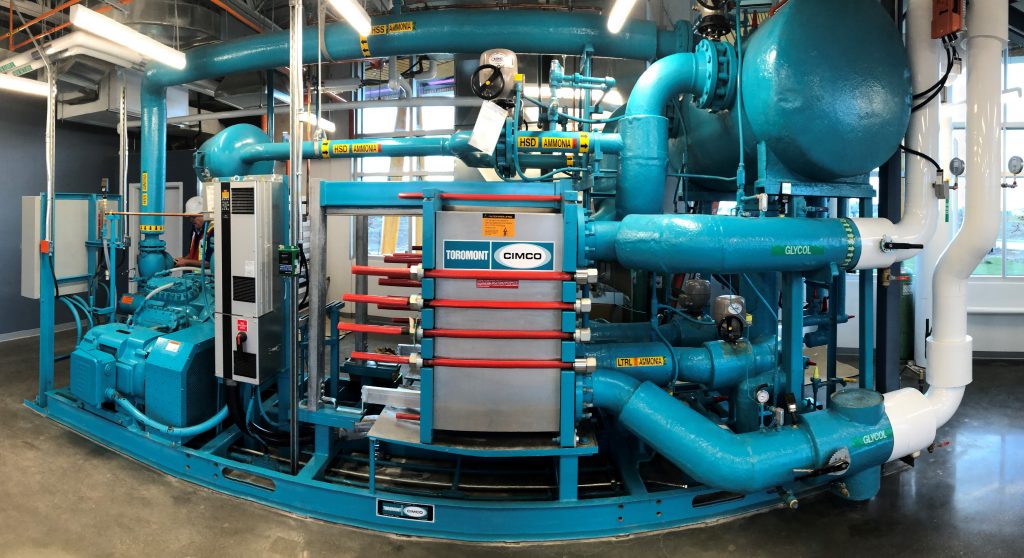
The system makes use of on-site renewable energy sources including a 570 borehole geoexchange field (completed in 2019) and a sewer heat recovery energy centre (in design) which will recover low-grade heat from an existing 2100mmØ sewer trunk running under the site. The City’s target is to provide 100% renewable energy to the community of 30,000 residents through the DESS and electrification of heating loads. The DESS provides all heating, cooling and domestic hot water to a variety of building types including townhouses, condos, and mixed-use buildings.
Planning and Design of the Project
Pinchin continues to provide support to the City of Edmonton throughout all aspects of the project development. Our comprehensive assistance includes:
- Conceptual design and feasibility assessment
- Business case assessment
- Energy utility bylaw, regulations, and rate development
- Utility master planning
- Detailed engineering design and construction administration
- Operations and maintenance support
- Design of Energy Transfer Stations and review of customer building HVAC systems
Additional Information
To learn more about how Pinchin helps in Alternative Energy, visit Alternative Energy (pinchin.com) or contact our experts listed below.
For more details about the City of Edmonton Blatchford project and for the latest updates, please visit – News | Blatchford | City of Edmonton (blatchfordedmonton.ca)


Working Together, Making Things Better
Meet the Pinchin Team

National Practice Leader
Mechanical Division
Practice Line: Mechanical Engineering & Design (MEC)

Senior Technical Manager, Alternative Energy
Practice Line: Mechanical Engineering & Design (MEC)
If you are interested working with our team, look for employment opportunities here: Employment Opportunities (pinchin.com)
Pinchin Services
Contact us to learn more about Pinchin Services.